Working with industry to co-develop industry-ready tools
Introduction
CSIC with industry partner, Mott MacDonald, jointly funded two six-month secondment projects for Mott MacDonald staff to join CSIC’s asset management team to create industry-ready tools from existing CSIC research. These secondments are part of the CSIC Industry Secondment Programme, funded by Innovate UK and industry partners, which offers six to 12 month secondments, tailored to meet both the needs of the seconding organisation and CSIC’s research, development and deployment programme. These two secondments took place from October 2017 through to March 2018 and resulted in two tools ready for industry uptake – BIM maturity assessment tool and Bridge maintenance optimisation tool.
Extending BIM maturity assessment tool to Digital Built Britain Level 2
CSIC’s BIM Maturity Assessment Tool
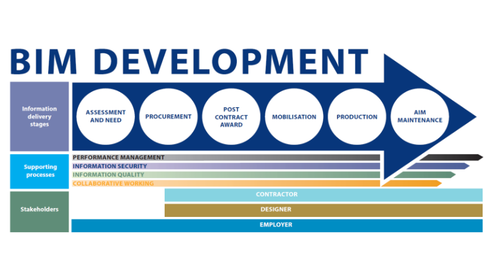
Since 2016, all UK government procured projects require Level 2 BIM. CSIC’s BIM Maturity Assessment Tool (BMAT), initially developed in 2017, uses established performance measurement practices, BIM literature, and other relevant standards, to build and expand on previous BIM assessment tools. Consisting of two major parts – measurement of the organisation’s BIM development maturity and measurement of the supporting processes – the tool provides a separate assessment of the different stakeholders (contractor, designer and employer), and is designed to be used as a continuous performance measurement tool that can be employed to track the evolution of BIM maturity throughout the construction phase through to handover. The Excel-based tool is designed to be user-friendly and adaptable to the needs of individual organisations and projects. Limited testing of the tool was successful but more case studies were needed for validation.
Secondment project – BIM Maturity Assessment Tool
This aim of the secondment project was to ensure the tool complies with all of the applicable standards1, to validate the tool through five additional cross-sector case studies and to ensure its appropriateness for Level 2 BIM maturity assessments. Also, the tool required future-proofing for extension beyond Level 2.
In order to develop the tool and make it effective and useful to industry, diverse case studies were identified from a range of sectors (water, railways, highways, and nuclear) and various stages in the project delivery cycle (design, construction and handover) as well as different contract types (e.g. traditional, and, design and build). The updated tool is structured to ask the right questions of the user depending on the stage of the Information Delivery Cycle (IDC) and which stakeholders are involved. The tool is designed to reveal how well the asset owner has defined the asset information requirements and how well the different project stakeholders have defined their approach to develop these requirements for both the BIM Execution Plan (BEP) and the Master Information Delivery Plan (MIDP). The tool enables clarity on who owns the data, who owns the common data environment, and who will take responsibility for the Asset Information Model (AIM) upon handover. Questions are asked about competency and information production, which standards have been applied, how to measure the quality of data used, and how the different stakeholders collaborate.
Next steps
The tool is designed to be extended further. Plans include testing additional case studies and improving the weighting system and interdependencies between the various BIM elements, as well as the development of a web-based version which will enable widely processing and disseminating maturity assessment results across the country.
An industry-ready tool for optimising maintenance activities across multiple bridges throughout their lifetime
CSIC‘s Predictive Maintenance Model
CSIC researchers have developed a methodology to help asset managers to determine the most optimal timing for interventions on their bridge portfolio in a predictive manner. As maintenance budgets for bridge systems are squeezed, many necessary maintenance activities are delayed or cancelled. Retaining an appropriate level of service and safety for an infrastructure network has become a challenging issue and there is pressing need for a smart asset management approach for road bridges.
The structure of the overall approach is composed of five interconnected models: deterioration model; lifecycle cost model; predictive maintenance; group maintenance; and maintenance scheduling model (Figure 2 - download the full case study to see figures). The deterioration model is formulated for each component of the bridges based on the information from the Structures Asset Management Planning Toolkit, general inspection, and other theoretical models. The predictability of the maintenance model enables proactive grouping of maintenance activities at different timings to reduce add-on costs such as the cost of preliminaries, traffic management and design. These add-on costs can be up to 80 per cent of the cost of repairs that are carried out at the same time. Finally, a genetic algorithm is developed to schedule the maintenance under the budget. The methodology was initially applied on a case study with Hertfordshire County Council on the Hailey Link and Stansted road bridges along the A10.
Secondment project – Bridges Asset Management Toolkit
Through this secondment an industry-ready tool has been developed based on the CSIC approach that provides industry focus to assist in making the tools practical and usable by the end user, e.g. the asset manager or consultant acting on their behalf. The output is designed to be meaningful and supports asset management planning and business case development for the asset owner, as well as the interface between the Structures Asset Management Toolkit and asset management systems to allow asset data input to be automated. The tool is designed to be used for any type of bridge from footbridges to motorway bridges. It has been tested and demonstrated using real industry data and dependencies and, constraints have been tested to enable scenario planning.
Next steps
To develop the CISC toolkit, data including deterioration rates and maintenance costs were extracted from the 2015 update of the Structures Asset Management Toolkit Documentation published by the Department for Transport. This data is different from the current version of the DfT Strcutures Asset Management Toolkit released in 2017. Therefore, it is difficult to compare the CSIC toolkit results against the DfT toolkit. The latest data are required in order to secure more accurate results and also validate the outcome of the CSIC toolkit. The available tools in the market have a time-dependent strategy based on experience. The CSIC tool is the first to provide a strategy based on data using a mathematical model to reduce the maintenance costs and improve the safety of bridges at the same time; the CSIC tool introduces a cost and safety dependent maintenance strategy. The tool can be used for a wide range of applications within the infrastructure sector. The next step is to make the tool adaptable for different types of assets such as tunnels, retaining walls, and earthworks.
Secondment programme
Our secondment programme offers benefits to all stakeholders. Secondees bring new skills, projects and challenges to CSIC that help to develop emerging tools and technologies for industry use. The secondees gain a deep understanding of innovations which they can apply for the direct benefit of their own companies/organisations.
CSIC team: Dr Ajith Parlikad, Dr Zhenglin Liang
Industry: Alex Gkiokas, Secondee – BIM Maturity Assessment Tool, Mott MacDonald, Dr Hooman Atefi, Secondee – Bridges Asset Management Toolkit, Mott MacDonald
